Disorders of epidermal appendages are abnormalities of the skin epidermal layer and its components.
Examples of disorders of epidermal appendages include:
- Acne vulgaris
- Rosacea
What is Acne Vulgaris?
Acne vulgaris is a common chronic skin illness involving impasse or inflammation of pilosebaceous components.
What is the Pathology of Acne Vulgaris?
The pathology of acne vulgaris is:
-Etiology: The cause of acne vulgaris is a genetic predisposition, some cosmetic agents.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to acne vulgaris is incompletely understood.
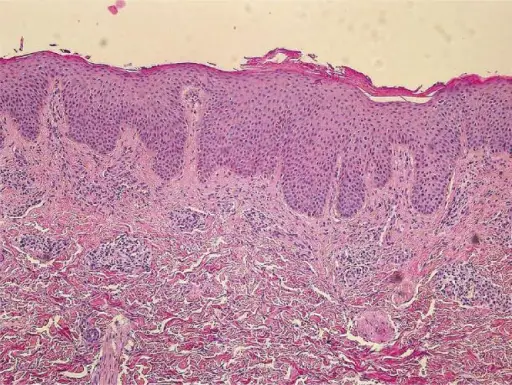
-Morphology: The morphology associated with acne vulgaris shows plug dense keratin dilated follicle, fibrosis, and scarring.
-Histology: The histology associated with acne vulgaris shows dense inflammatory infiltrate.
How does Acne Vulgaris Present?
Patients with acne vulgaris typically tend to be more in males than females present at an age range of 12 to 24. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with acne vulgaris include open/closed noninflammatory comedones, nodules, and pustules.
How is Acne Vulgaris Diagnosed?
Acne vulgaris is diagnosed through physical examination, laboratory studies.
How is Acne Vulgaris Treated?
Acne vulgaris is treated through medical care include androgen receptor antagonists, retinoid, antimicrobial therapy, hormonal therapies. Surgical care intralesional steroid injections, light, and laser therapy.
What is the Prognosis of Acne Vulgaris?
The prognosis of acne vulgaris is good. Though may lead to long-lasting and detrimental psychosocial and physical effects.