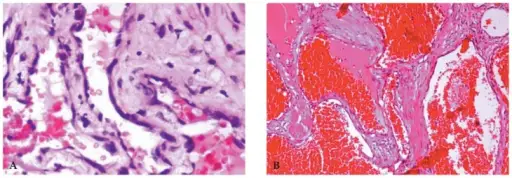
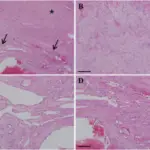
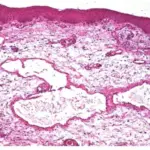
Encapsulated cavernous hemangiomas medical conditions involving dilated endothelial lined vascular channels filled with slowly flowing fluid.
What is the Pathology of Encapsulated Capillary Hemangiomas?
The pathology of encapsulated capillary hemangiomas is Encapsulated nodular mass of inflamed vascular tissue. Tumor growth is a result of budding of the vascular channels into the surrounding soft tissues.
How do Encapsulated Capillary Hemangiomas Present?
Encapsulated capillary hemangiomas present with osseous lesion, unilateral lesion, solitary lesions.
How are Encapsulated Capillary Hemangiomas Diagnosed?
Encapsulated capillary hemangiomas are diagnosed by physical examination, family history, X-ray, orbital echography, tonometry, and susceptibility weighted imaging.
How is Encapsulated Capillary Hemangiomas Treated?
Encapsulated capillary hemangiomas are treated with craniotomy, stereotactically assisted craniotomy, and stereotactic radiosurgery.
What is the Prognosis of Encapsulated Capillary Hemangiomas?
The prognosis of encapsulated capillary hemangiomas is excellent vision prognosis in a case of surgical excision although hyperopia may persist as a result of mass effect against the posterior globe. Recurrence may occur in the case of incomplete excision.