Forebrain anomalies are malformations of the forebrain most commonly due to chromosomal abnormalities, fetal alcohol syndrome, and HIV-1 infection acquired in vitro.
Examples of forebrain anomalies include:
- Agenesis of the corpus callosum
- Holoprosencephaly
- Arrhinencephaly
- Microencephaly
- Macroencephaly
- Lissencephaly
- Polymicrogyria
- Neuronal heterotopias
What is Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum?
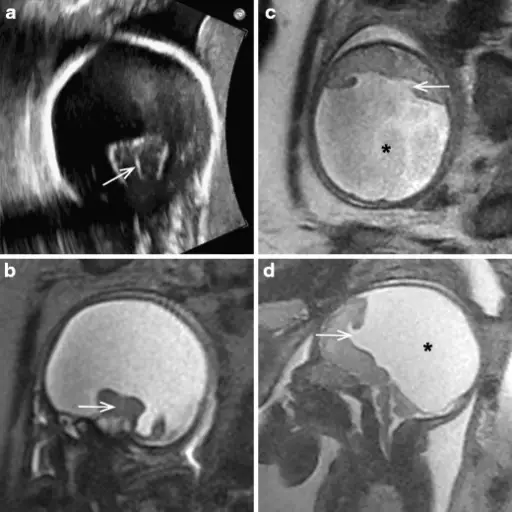
Agenesis of the corpus callosum is a rare birth defect in which there is a partial or complete absence of the corpus callosum. Agenesis of the corpus callosum results when the development of the corpus callosum is disrupted.
What is Holoprosencephaly?
Holoprosencephaly is a rare congenital brain malformation resulting from incomplete separation of the two hemispheres. The three main subtypes of holoprosencephaly in order of decreasing severity are:
- Alobar holoprosencephaly
- Semilobar holoprosencephaly
- Lobar holoprosencephaly
What is Arhinencephaly?
Arhinencephaly is a rare non-syndromic central nervous system malformation defined by the agenesis of the olfactory bulbs and tracts. Arhinecephaly causes congenital anosmia (lack of smell).
What is Microcephaly?
Microcephaly is a rare neurological condition in which an infant’s head is significantly smaller as compared with that of the other children of the same age and sex. Microcephaly can result from the brain developing abnormally in the womb or not growing as it should after birth. A variety of genetic and environmental factors can cause this microcephaly.
What is Macrocephaly?
Macrocephaly is a condition in which the head circumference is more than two standard deviations above the mean for gestational age and sex.
What is Lissencephaly?
Lissencephaly is a rare, gene-linked brain malformation characterized by the absence of normal folds and convolutions in the cerebral cortex and microcephaly. Children with lissencephaly usually have a normal sized head at birth.
What is Polymicrogyria?
Polymicrogyria is a condition characterized by abnormal development of the brain prior to birth. Polymicrogyria has too many unusually small folds.
What are Neuronal Heterotopias?
Neuronal heterotopias are brain malformations that result from deficits of neuronal migration. Individuals with neuronal heterotopias show a high incidence of neurological deficits, such as confusion, altered mental status, and epilepsy.