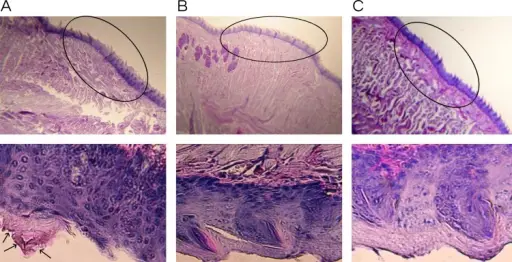
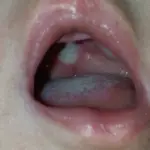
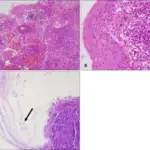
Fungal infections of the oral cavity are the fungal infections that manifest within the oral cavity
Examples of fungal infections of the oral cavity include:
- Deep fungal infections
- Aspergillosis
- Blastomycosis
- Coccidioidomycosis
- Cryptococcosis
- Histoplasmosis
- Zygomycosis
| FUNGAL INFECTION | HISTOLOGY | PRESENTATION | TREATMENT | PROGNOSIS |
| ASPERGILLOSIS | Hyphae that are uniform, narrow (3 to 6 micrometers in width), tubular, and regularly septate. Branching is regular, progressive, and dichotomous. | Fever, cough, dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, and sometimes hemoptysis in patients with prolonged neutropenia or immunosuppression. Aspergillus infection after organ transplantation most often occurs in bone marrow recipients. | Oral corticosteroids, Antifungal medications, Surgery | Prognosis is poor |
| BLASTOMYCOSIS | Broad verrucous lesion with epidermal papillomatosis which may resemble a keratoacanthoma. There may be surface erosion and suppuration. Numerous cystic spaces connect with the surface via draining sinuses. | Flu-like illness with fever, chills, myalgia, headache, chest pain, and a nonproductive cough | Antifungal medication. | Variable |
| COCCIDIOIDOMYCOSIS | Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia of epidermis and adjacent or admixed acute suppurative inflammation. Variable infiltrate of neutrophils, eosinophils, histiocytes, multinucleated giant cells, plasma cells and rarely lymphocytes are present· | Reactive and organism-specific reactive manifestations do not contain visible microorganisms and may exhibit features of erythema nodosum, Sweet syndrome, and interstitial granulomatous dermatitis. Rarely, patients may exhibit features of erythema multiforme, acute generalized exanthema, secondary to hypersensitivity to systemic infection | Fluconazole or another type of antifungal medication. | Good |
| CRYPTOCOCCOSIS | Variably sized (3.5 – 8 μm in diameter)· Round to oval encapsulated yeasts with thin cell walls· | ·Opportunistic infection· | Liposomal amphotericin B | Good |
| HISTOPLASMOSIS | Yeast forms (2 – 5 um) with basophilic crescent-shaped nuclei | Diarrhea, bleeding, pain, nausea, vomiting, flu-like symptoms | Itraconazole Amphotericin for disseminated disease | Variable |
| ZYGOMYCOSIS | Coagulative necrosis due to fungi with broad, sparsely septate, thin-walled hyphae· | Necrosis | Amphotericin B or newer drugs· Surgical debridement | Poor prognosis |