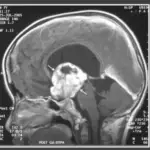
Gliomas are tumor lesions mostly occurring in the brain stem within the pons, midbrain, and medulla, which may infiltrate past the brainstem.
What is the Pathology of Gliomas?
The pathology of gliomas is:
-Etiology: The cause of gliomas is genetic or environmental.
-Genes involved: PDGF-A, RB gene, the p16/CDKNZA gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to gliomas, not well known.
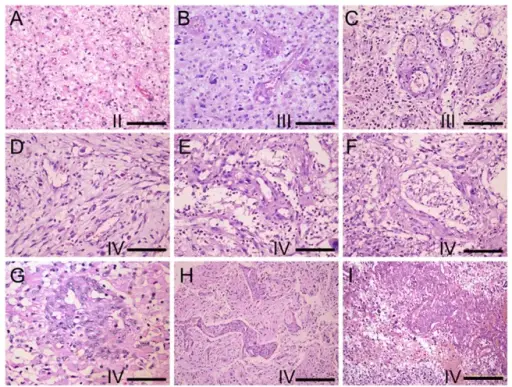
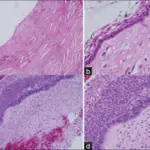
-Morphology: The morphology associated with gliomas shows differentiated (astrocytoma) or less differentiated (higher-grade), ranging from anaplastic astrocytoma to glioblastoma, range in size from a few centimeters to enormous lesions.
-Histology: The histology associated with gliomas shows noticeable hypercellularity, microvascular proliferation, nuclear atypia, and necrosis.
How does Gliomas Present?
Patients with gliomas typically have no gender prevalence present at an age range of 10 to 60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with gliomas include unsteady gait, dysarthria, dysphagia, drowsiness, headache, rare seizures, failure to thrive, long tract signs, and ataxia.
How are Gliomas Diagnosed?
Gliomas are diagnosed through laboratory studies including CSF examination.
How is Gliomas Treated?
Gliomas are treated through surgical resection, radiotherapy, or chemotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Gliomas?
The prognosis of gliomas is good, with longer survival allied to the tectal and cervicomedullary gliomas. Poor prognosis allied to intrinsic pontine gliomas with a 5-year relative survival of 5%.