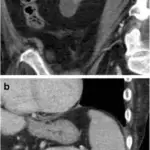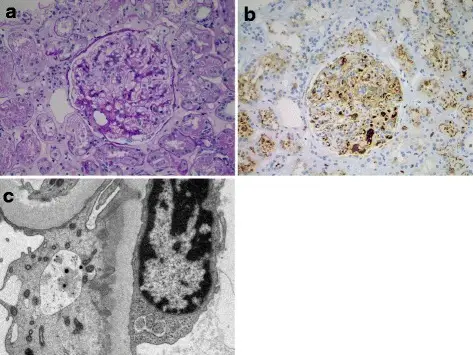
IgG4-related membranous glomerulonephropathy. a Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stain of a case of clinically confirmed IgG4-related kidney disease (IgG4-RKD, same patient as in Fig. 1), showing a membranous pattern of glomerulonephropathy with occasional plasma cells in the mesangium. b IgG4 immunohistochemistry confirming several IgG4 expressing plasma cells in the glomerulus. c Electron microscopy demonstrating subepithelial electron-dense deposits, consistent with membranous glomerulonephropathy. Recognizing IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis: Mann S, Seidman MA, Barbour SJ, Levin A, Carruthers M, Chen LY - Canadian journal of kidney health and disease (2016). Not altered. CC.
Glomerular diseases are anomalies of the glomerular part of the kidney constituting major problems in nephrology.
Glomerular disease may be due to one or more of the following:
- Activation of alternative complement pathway
- Antibodies against components of the glomerular basement membrane
- Cell-mediated immunity in glomerulonephritis
- Deposition of circulating immune complexes
- Epithelial cell injury
- In situ formation of immune complexes
- Glomerular injury following immune complex formation
Examples of glomerular disease include:
- Nephrotic syndromes
- Nephritic syndromes
- Isolated glomerular abnormalities
- Chronic glomerulonephritis