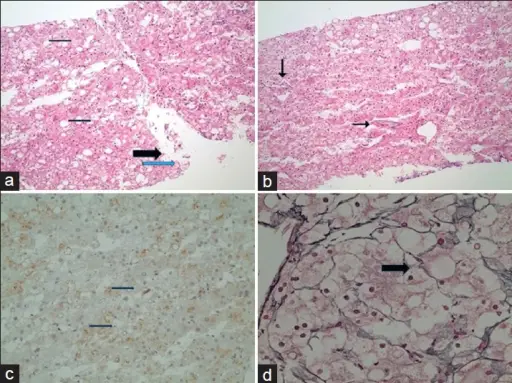
Glycogen storage diseases are group of diseases resulting in abnormal glycogen metabolism and an accumulation of glycogen within cells.
Examples of glycogen storage disease include:
Types I, II, III, IV, and V.
| Types | Affected tissue | Enzyme defect | Clinical features | Tissue needed for diagnosis* | Outcome |
| Von Gierke disease (type I) | Liver, intestine, kidney | Glucose-6-phosphatase | Hepatomegaly, hypoglycemia, stunted growth, obesity, hypotonia | Liver | If patient survive initial hypoglycemia, prognosis is good; hyperuricemia is a late complication |
| Pompe disease (type II) | Liver, muscle, heart | Lysosomal acid α-1,4-glucosidase with α-1,6-glucosidase activity | Cardiomegaly, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, hypotonia, exercise intolerance, and systemic findings. | Leukocytes, liver, muscle | Death in first 6 months; juvenile and adult variants seen |
| Forbes disease (type III) | Liver, muscle (abnormal glycogen structure) | Amylo-1, 6-dlucosidase | Hepatomegaly, hypoglycemia, stunted growth, obesity, hypotonia | Leukocytes, liver, muscle | Good prognosis |
| Anderson disease (type IV) | Liver, (abnormal glycogen structure) | 1,4-α-glucan branching enzyme | Failure to thrive, hepatomegaly, cirrhosis and its complications | Leukocytes, liver, muscle | Death in first 3 years |
| McArdle disease (type V) | Muscle only | Phosphorylase | Muscle cramps and myoglobinuria after exercise (in adults) | Muscle | Normal lifespan; exercise must be avoided |