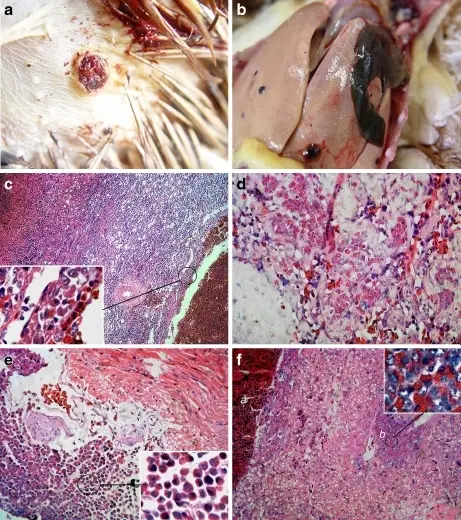
Hemangiomas are bright red birthmarks that show up at birth or in the first or second week of life. They look like a rubbery bump and are made up of extra blood vessels in the skin. A hemangioma can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly appears on the face, scalp, chest or back.
What is the Pathology of Hemangiomas?
The pathology of hemangiomas is:
–Etiology: The cause of hemangiomas is an abnormal proliferation of blood vessels in one area of the body and caused by certain proteins produced in the placenta during gestation.
–Genes involved: Somatic mutations in VEGFR2, VEGFR3 (FLT4; 136352), and DUSP5 (603069) genes.
–Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to hemangiomas are vascular proliferation due to an imbalance of angiogenic factors and an increase in the levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloproteinases.
–Morphologic changes: The morphologic changes involved with hemangiomas are red-purple areas on the skin due to proliferation of vessels like capillaries.
How do Hemangiomas Present?
Patients with hemangiomas are typically females. Infantile hemangiomas usually become noticeable by 4 weeks of age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with hemangiomas are usually only cosmetic. Hemangiomas appear as small red scratches or bumps. As they grow, they look like burgundy-colored birthmarks. Skin hemangiomas are sometimes called strawberry hemangiomas because of their deep red appearance. Hemangiomas are the most common tumor of the young children.
How are Hemangiomas Diagnosed?
Hemangiomas of the skin are diagnosed by visual inspection, and histopathology to assess for vasculature proliferation. Hemangiomas may also occur in the organs such as the liver, and the diagnosis would utilize radiographic techniques (ultrasound, MRI, CT scan) and potentially a biopsy for definitive diagnosis.
How are Hemangiomas Treated?
Hemangiomas may regress on there own, be surgically removed for cosmetic reasons. Other treatments include beta-blockers, corticosteroid medication, medicated gel, and laser treatment.
What is the Prognosis of Hemangiomas?
The prognosis of hemangiomas is very good. Overtime hemangiomas may resolve on their own.