Infections involving the upper and lower genital tract include endometritis, salpingitis, peritonitis, pelvic abscess and septicemia of the upper tract, bacterial vaginosis, vaginal candidiasis, etc of lower genital tract.
What are Infections Involving the Upper and Lower Genital Tract?
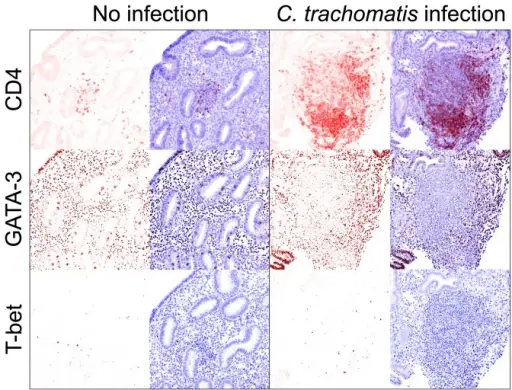
Endometrial Chlamydia infection is associated with thepresence of CD4+ T cell aggregates and high expression ofthe TH2 transcription factor GATA-3.Sequential sections of paraffin-embedded endometria from women with noidentified C. trachomatis, N. gonorrhoeae,or T. vaginalis lower or upper genital tract infection(n = 4) or with endometrial C.trachomatis infection (n = 6) were used toimmunohistochemically evaluate T-bet or GATA-3 expression (both DAB), andthe presence of CD4+ mononuclear cells (Vector Red) asdescribed in Methods section. Aggregates of GATA-3+ (but notT-bet+) and CD4+ mononuclear cells wereseen in endometrial stroma of Chlamydia-infected tissue(representative micrographs shown at X200 magnification). Moreover, only afew CD4+ mononuclear cells were present in uninfectedendometrial tissue even tough GATA-3 was expressed at high levels in bothinstances. Right panels show images displaying DAB or Vector Red stainingand hematoxylin as counterstain, while left panels show DAB or Vector Redlayer alone. Human female genital tract infection by the obligate intracellular bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis elicits robust Type 2 immunity. Vicetti Miguel RD, Harvey SA, LaFramboise WA, Reighard SD, Matthews DB, Cherpes TL - PloS one (2013). Not Altered. CC.