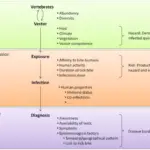
Infectious diseases are disorders caused by living organisms. Infectious organisms include viral infections, bacterial infections, fungal infections, and parasitic infections.
WHAT ARE INFECTIOUS DISEASES?
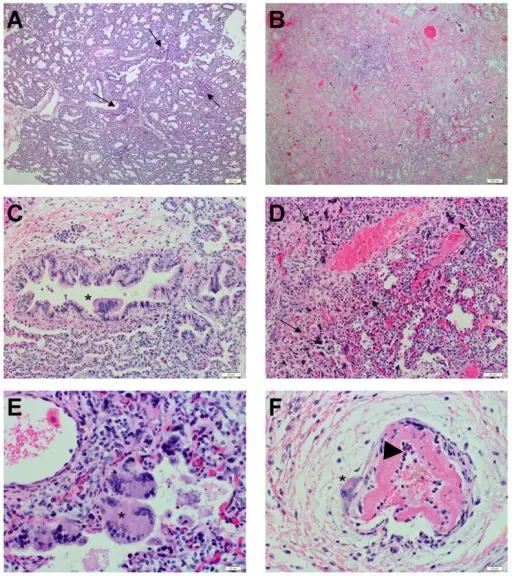
(A) Human lung with focal areas of necrosis and syncytia formation (black arrow) on day 3 post infection (10× magnification). (B) Human lung with extensive areas of necrosis, syncytia formation and loss of architecture on day 10 post infection (10× magnification). (C) Bronchi with syncytia formation (*) on day 3 post infection (20× magnification). (D) Loss of alveolar architecture and areas of necrosis (black arrow) on day 10 post infection (20× magnification). (E) Alveolar space with syncytial formation (*) on day 3 post infection (40× magnification). (F) Pulmonary vasculature with syncytial formation (*) on day 3 post infection (40× magnification), fibrinoid necrosis of the intima, and influx of granulocytes (black arrowhead). A human lung xenograft mouse model of Nipah virus infection: Valbuena G, Halliday H, Borisevich V, Goez Y, Rockx B - PLoS pathogens (2014). Not altered. CC.