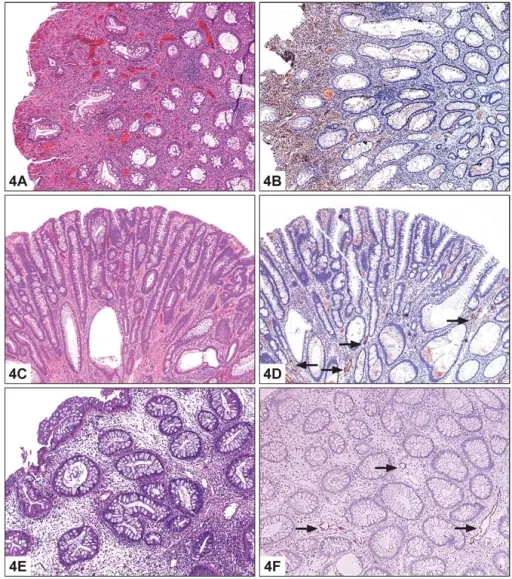
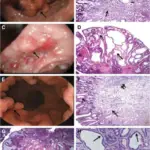
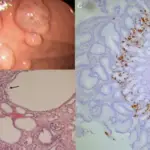
Inflammatory polyps are non-neoplastic intraluminal projections of mucosa consisting of stromal and epithelial components and inflammatory cells. Inflammatory polyps include inflammatory pseudopolyps and prolapse type inflammatory polyps.
What is the Pathology of Inflammatory Polyps?
The pathology of inflammatory polyps is:
-Etiology: The cause of inflammatory polyps is inflammatory intestinal conditions, such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease of the colon, smoking and excess alcohol use, obesity, lack of exercise and fat intake.
-Genes involved: GSE136825, GSE36830.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to inflammatory polyps were derived from polypoid mucosal tags after regeneration and the adjacent mucosa showed regenerative changes and submucosal scarring. The study confirms that ulceration which undermines the muscularis mucosae is the major precursor of inflammatory polyps.
-Histology: The histology associated with inflammatory polyps shows in children are predomination of the inflammatory component represented by granulation tissue.
How does Inflammatory Polyps Present?
Patients with inflammatory polyps typically more in male at 50 years older ages. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with inflammatory polyps include rectal bleeding, change in bowel habits, abdominal pain, and anemia.
How is Inflammatory Polyps Diagnosed?
Inflammatory polyps is diagnosed by colonoscopy, and biopsy.
How is Inflammatory Polyps Treated?
Inflammatory polyps are treated by medications, and removal of polyps.
What is the Prognosis of Inflammatory Polyps?
The prognosis of inflammatory polyps is good. Inflammatory polyps are benign and generally do not carry the risk of developing into colon cancer.