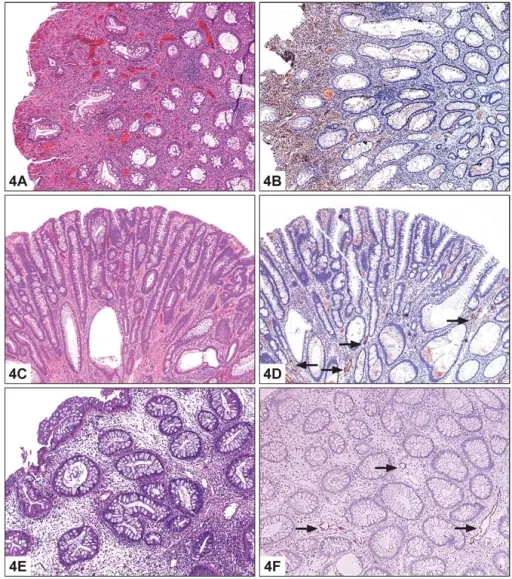
Inflammatory polyps are non-neoplastic intraluminal projections of mucosa consisting of stromal and epithelial components and inflammatory cells.
What is the Pathology of Inflammatory Polyps?
The pathology of inflammatory polyps is:
-etiology: the cause of inflammatory polyps is inflammatory intestinal conditions, smoking and excess alcohol use, obesity, lack of exercise and fat intake.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to inflammatory polyps are polypoid mucosal tags after regeneration and the adjacent mucosa showed regenerative changes and submucosal scarring.
-Histology: The histology associated with inflammatory polyps shows predomination of the inflammatory component represented by granulation tissue and does not contain glands but may contain foreign bodies and giant cells.
How does Inflammatory Polyps Present?
Patients with inflammatory polyps typically are all genders with age 50 years of age or older. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with inflammatory polyps include change in bowel habits, pain, iron deficiency anemia.
How is Inflammatory Polyps Diagnosed?
Inflammatory polyps is diagnosed by colonoscopy, CT scan, and biopsy.
How is Inflammatory Polyps Treated?
Inflammatory polyps is treated by surgery and medication.
What is the Prognosis of Inflammatory Polyps?
The prognosis of inflammatory polyps is good. These types of polyps are also known as pseudopolyps because they are not true polyps, but rather develop as a reaction to chronic inflammation in the colon.