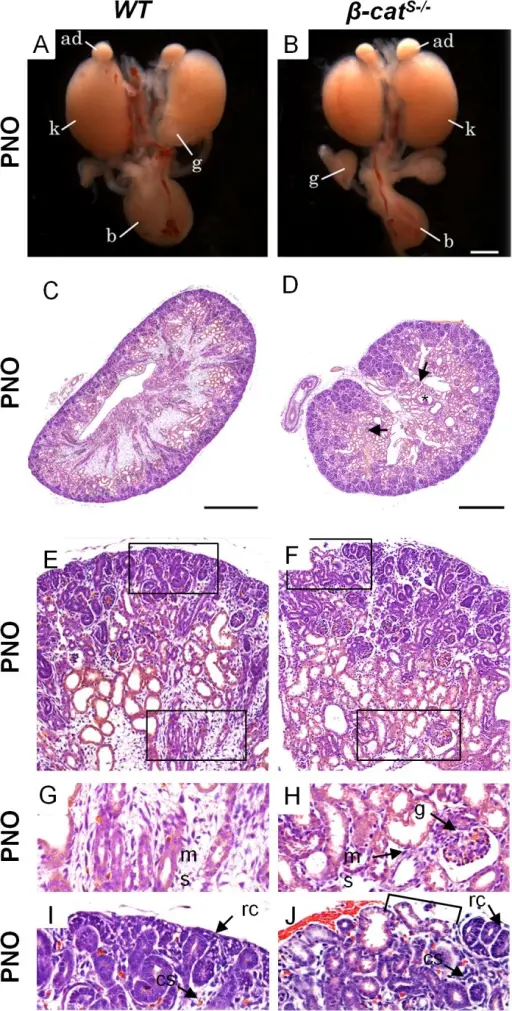
β-catS-/- mutants demonstrate multiple kidney abnormalities. (A, B) The gross anatomy of PN0 WT and β-catS-/- kidneys show comparable size and shape. (C-J) In contrast to WT, histological analysis of β-catS-/- mutant kidneys demonstrate numerous kidney abnormalities. (C,D) As compared to WT, β-catS-/- mutant kidneys were lobular, lacked a distinct boarder, contained numerous cysts in the medulla and cortex (star), with an ill-defined cortical medullary axis and misplaced glomeruli (arrow). (E-J) In contrast to WT, high magnification of β-catS-/- kidneys at PN0 revealed a non-adherent sporadic renal capsule (F and J), misplaced tubules just under the renal capsule (F and J), glomeruli in the medulla (H), and a marked reduction in the medullary stroma (H). (A, B scale bar = 1mm, C, D scale bar = 100μm, ad = adrenal gland, k = kidney, b = bladder, rc = renal capsule, cs = cortical stroma, ms = medullary stroma, g = glomerulus). Stromally expressed β-catenin modulates Wnt9b signaling in the ureteric epithelium: Boivin FJ, Sarin S, Lim J, Javidan A, Svajger B, Khalili H, Bridgewater D - PloS one (2015). Not altered. CC.
Isolated glomerular abnormalities are diseases of the kidney that occur as a result of genetic factors
Examples of isolated glomerular abnormalities include:
- Hereditary nephritis
- IgA nephropathy (Berger disease)
