Juvenile hemangiomas are benign vascular neoplasms with characteristic clinical progression manifested by early proliferation and then tailed by spontaneous involution.
What is the Pathology of Juvenile Hemangiomas?
The pathology of juvenile hemangiomas is:
-Etiology: The cause of juvenile hemangiomas is unknown.
-Genes involved: VEGFR1.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to juvenile hemangiomas not well elucidated
-Morphology: The morphology associated with juvenile hemangiomas shows the quantity of fibrofatty tissue.
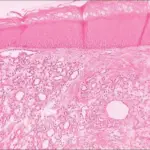
-Histology: The histology associated with juvenile hemangiomas shows nonencapsulated masses plump endothelial cells.
How does Juvenile Hemangiomas Present?
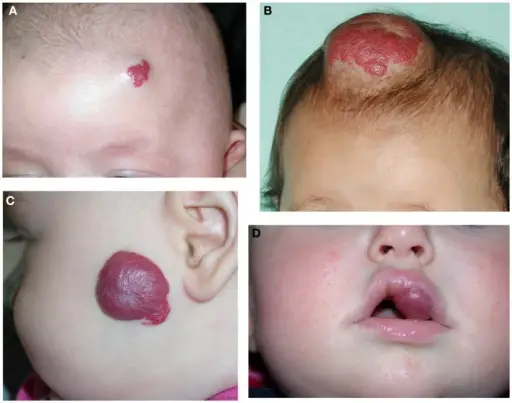
Patients with juvenile hemangiomas, typically females, are more affected than males present at birth to 9 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with juvenile hemangiomas include blanching of skin, red/crimson macule, shallow ulceration.
How is Juvenile Hemangiomas Diagnosed?
Juvenile hemangiomas is diagnosed through the clinical presentation, laboratory studies. Skin biopsy is diagnostic.
How is Juvenile Hemangiomas Treated?
Juvenile hemangiomas is treated through medical care such as propranolol and corticosteroid therapy. Surgical interventions such as laser surgery and surgical excision.
What is the Prognosis of Juvenile Hemangiomas?
The prognosis of juvenile hemangiomas is good.