Hilus cell tumors aka pure leydig cell tumors are uncommon branch of androgen producing neoplasms which are mostly benign and have characteristic gross and microscopic features.
What is the Pathology of Leydig Cell Tumors?
The pathology of hilus cell tumors is:
-Etiology: The cause of hilus cell tumors is unknown.
-Genes involved: DICER1 gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to hilus cell tumors are unknown.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with hilus cell tumors shows unilateral lesions.
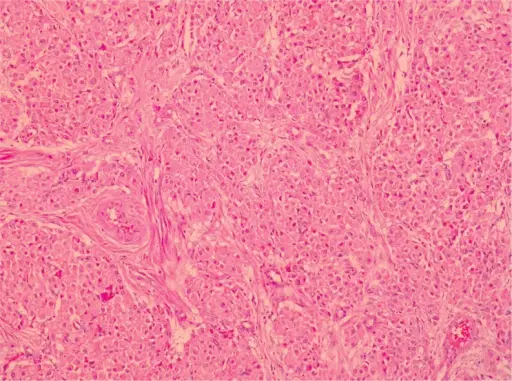
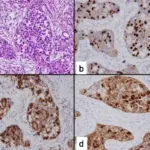
-Histology: The histology associated with hilus cell tumors shows large lipid laden cells with distinct borders. Reinke crystals are common.
How does Leydig Cell Tumors Present?
Patients with hilus cell tumors typically in females 32 to 82 years of age range. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with hilus cell tumors include intestinal obstruction, virilization, hirsutism, baldness, deeping of voice, clitoromegaly, and amenorrhea.
How is Leydig Cell Tumors Diagnosed?
Hilus cell tumors is diagnosed by: microscopic examination, blood test for testosterone levels, ultrasound, CT scan.
How are Leydig Cell TumorsTreated?
Hilus cell tumors is treated by: laparotomy, Total hysterectomy and bilateral salpingoophorectomy.
What is the Prognosis of Leydig Cell Tumors?
The prognosis of hilus cell tumors is good after excision.