Lipomas are slow-growing, benign fatty growths.
What is the Pathology of Lipomas?
The pathology of lipomas is:
-Etiology: The cause of lipomas is unclear, nonetheless may imitate growth of local pluripotent cells into adipocyte lines.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to lipomas involve adipocyte cell overproduction.
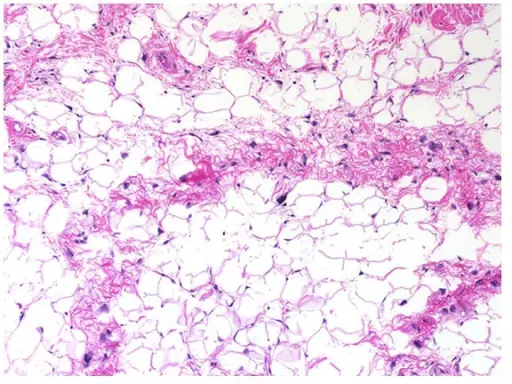
-Morphology: The morphology associated with lipomas shows fatty lesion on spermatic cord in this instance.
-Histology: The histology associated with lipomas shows benign adipose tissue comprising the entirety of the lesion.
How do Lipomas Present?
Patients with lipomas typically present at age range of 18 years and above. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with lipomas include pain tender, and soft bulging mass.
How are Lipomas Diagnosed?
Lipomas is diagnosed through clinical examination, imaging studies, and biopsy.
How are Lipomas Treated?
Lipomas are treated by surgical intervention.
What is the Prognosis of Lipomas?
The prognosis of lipomas is fair after surgical interventions.