Lipomas are benign tumors of fat and are the most common soft tissue tumors in adults.
What is the Pathology of Lipomas?
The pathology of lipoma is:
-Etiology: The precise cause of lipomas is unknown.
-Genes involved: HMGA2-LPP fusion gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to lipoma formation is still unclear.
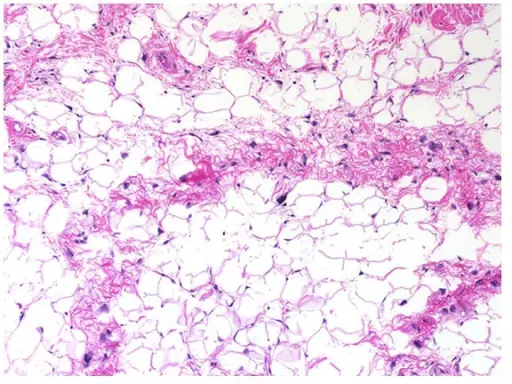
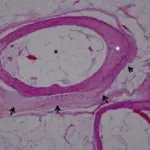
-Histology: The histology associated with lipoma shows mature, normal-appearing adipocytes with small eccentric nuclei.
How does Lipoma Present?
Patients with lipoma are typically males or females present at an age range of 40-50 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with lipoma include the following a soft tissue well-circumscribed nodule.
How is Lipoma Diagnosed?
Common lipomas frequently are diagnosed clinically and are sent for histologic examination after complete surgical excision.
How is Lipoma Treated?
Lipoma is usually treated by surgical excision.
What is the Prognosis of Lipoma?
The prognosis of lipoma is excellent for benign lipomas. Recurrence is uncommon but may develop if the excision was incomplete.