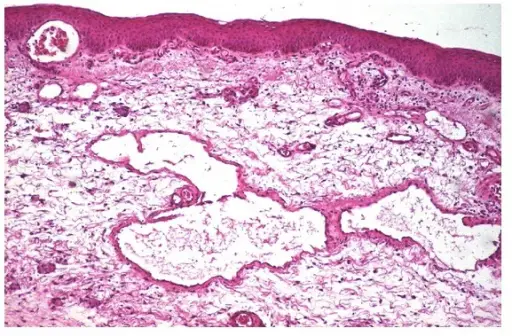
Lymphangiomas are common lymphatic tumors of the young. Lymphangiomas are also called lymphatic malformations. Lymphangiomas are noncancerous, fluid-filled cysts that occur in lymphatic vessels. These vessels contain a substance called lymph, and together they make up the lymphatic system. Lymph helps to properly regulate fluid in body tissue.
What is the Pathology of Lymphangiomas?
The pathology of lymphangiomas is:
–Etiology: The cause of lymphangiomas is abnormal development of the lymphatic channels. Cystic hygromas (cystic lymphangioma) may occur as part of a genetic syndromes such as Noonan syndrome, Turner syndrome and Down syndrome.
–Genes involved: Somatic mutations of the PIK3CA
–Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to lymphangiomas include failure of the lymphatic system to connect with or separate from the venous system, abnormal budding of the lymphatic system from the cardinal vein, or acquired processes such as traumata, infections, chronic inflammations, and obstructions.
–Morphologic changes: The morphologic changes involved with (lymphangiomas): swelling or mass that occurs mainly in the head, neck, and mouth.
How do Lymphangiomas Present?
Lymphangiomas do not have a gender preference. Lymphangioma can become evident at any age, but the greatest incidence occurs at birth or early in life. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with lymphangiomas are usually only cosmetic. Lymphangiomas may appear as tiny reddish or blue dots. As lymph accumulates, they can create significant and deforming swelling.
How are Lymphangiomas Diagnosed?
Lymphangiomas are diagnosed by physical examinatioin, ultrasound scan, MRI scan, CT scan, and biopsies.
How are Lymphangiomas Treated?
Lymphangiomas are may be treated by surgery, sclerotherapy, laser therapy or radiofrequency ablation
What is the Prognosis of Lymphangiomas?
The prognosis of lymphangiomas is excellent. Most lymphatic malformations that appear suddenly will decrease in size and pain without treatment, but rarely go away on their own.