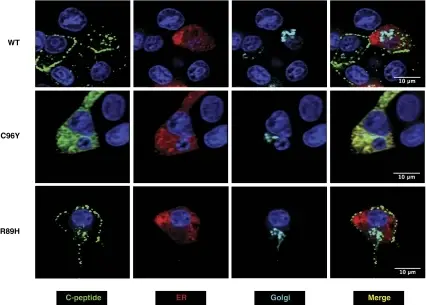
Monogenic Forms of Diabetes. Subcellular localization of wild-type (WT) and mutant human proinsulin expressed in rat INS-1 insulinoma cells [30]. The location of human C-peptide immunoreactive protein is shown in green, ER is shown in red and the Golgi marker in cyan. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). The WT and R89H hyperproinsulinemia mutant proinsulins are localized to secretory granules. By contrast, the C96Y PNDM-associated mutant proinsulin is localized to the expanded ER and is not transported from the ER to the Golgi and packaged into secretory granules. Clinical and molecular genetics of neonatal diabetes due to mutations in the insulin gene.
Støy J, Steiner DF, Park SY, Ye H, Philipson LH, Bell GI - Reviews in endocrine & metabolic disorders (2010). Not Altered. CC.
Monogenic forms of diabetes are subtypes of diabetes that occur due to mutation of the genes involved making the loos function.
Monogenic forms of diabetes include:
- Maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY)
- Diabetes due to insulin receptor defects
