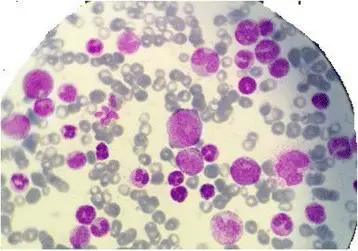
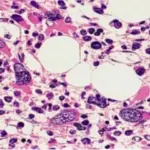
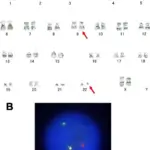
Myeloproliferative disorders are a group of hematopoietic stem cell disorders characterized by an abnormal proliferation of one or more hematologic cell lines (platelets, white blood cells and red blood cells).
Examples of myeloproliferative disorders include:
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia
- Polycythemia vera
- Essential thrombocythemia
- Primary myelofibrosis
- Systemic mastocytosis
- Chronic eosinophilic leukemia
| Myeloproliferative Syndrome | Genetics | Key Histologic Features | Key Clinical Findings |
| Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Philadelphia chromosome/translocation | Increased granulocytes and immature precursors | Enlarged spleen, weakness, fatigue, fever, bone pain, weight loss |
| Polycythemia vera | Point mutation in JAK2 gene | Bone marrow biopsy showing hypercellularity for age with trilineage growth (panmyelosis) including prominent erythroid, granulocytic and megakaryocytic proliferation with pleomorphic, mature megakaryocytes (differences in size) | Splenomegaly, headaches, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, excessive sweating at night, itchy skin |
| Essential thrombocythemia | JAK2, CALR, MPL gene mutation | Increase in bone marrow cellularity with megarkaryocytic hyperplasia | Headache, dizziness, chest pain, fainting, temporary vision changes, numbness or tingling of the hands and feet, redness, throbbing and burning pain in the hands and feet |
| Primary myelofibrosis | JAK2, CALR, MPL gene mutation | Hypocellular bone marrow with marked reticulin or collagen fibrosis. | Anemia, splenomegaly, general malaise, weight loss, fever, splenic infarction. |
| Systemic mastocytosis | KIT gene somatic mutation | Focal mast cell lesions in the bone marrow. | Flushing, itching or hives, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting, anemia or bleeding disorders |
| Chronic eosinophilic leukemia | Not linked to a specific gene or mutation | Striking eosinophilia in the peripheral blood and hypercellular bone marrow due to eosinophilic proliferation. | Fatigue, cough, dyspnea, myalgia, angioderma, rash, fever, rhinitis |