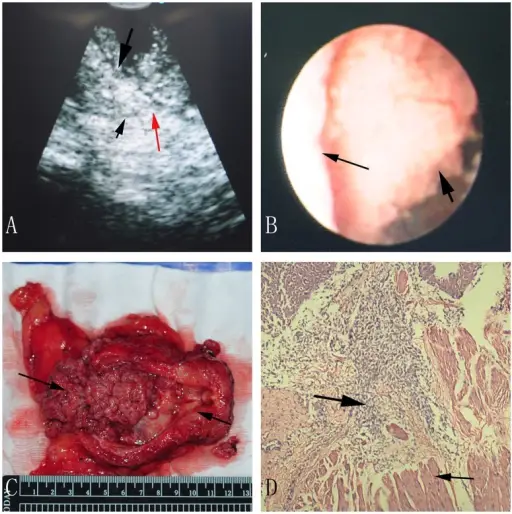
A muscle-invasive bladder tumor in ultrasonic image (A), direct version (B), radical cystectomy specimen (C) and pathological image (D).A: The big black arrow indicates bladder tumor, and the small black arrow indicates muscle layer, and the red arrow indicates uncontinuous muscle layer, and the blue arrow marked the bladder cavity; B: The big black arrow points at the bladder tumor, and the small one points at the bladder wall; C: The right arrow shows us a bladder tumor, and the left arrow shows us the bladder neck; D: The big black arrow indicates bladder tumor, and the small arrow indicates infiltrated muscle layer.A new tool for distinguishing muscle invasive and non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: the initial application of flexible ultrasound bronchoscope in bladder tumor staging.
Xu C, Zhang Z, Wang H, Song Q, Wei R, Yu Y, Li J, Sun Y - PloS one (2014). Not Altered. CC.
Neoplasms of the bladder are tumors that arise from the bladder layers.
Examples of neoplasms of the bladder include:
- Transitional tumors of the bladder
- Exophytic papillomas of the bladder
- Inverted papilloma of the bladder
- Papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential
- Low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma
- High grade papillary urothelial carcinoma
- Carcinoma in situ of the bladder
- Adenocarcinoma of the bladder
- Mixed carcinoma of the bladder
- Sarcoma of the bladder
- Small cell carcinoma of the bladder