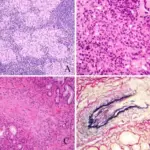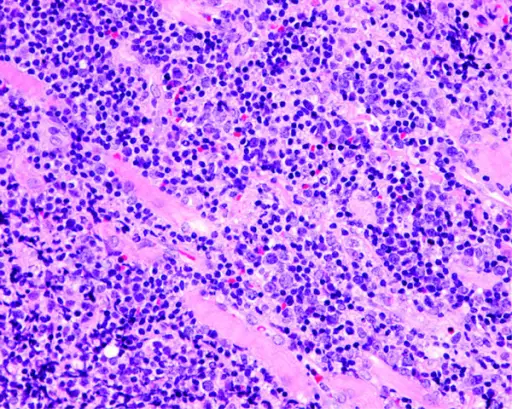
The resected orbital tumor shows infiltration of the extraocular muscles. Tumor biopsy was carried out six months after presentation. The tumor cells are large, polygonal, or round and the nuclei are folded, cleaved, or kidney-shaped. Mitoses and prominent nuclear abnormalities can be seen. The pathological diagnosis was diffuse large B cell lymphoma (hematoxylin-eosin, × 50). Unusual orbital lymphoma undetectable by magnetic resonance imaging: a case report.
Tatsugawa M, Noma H, Mimura T, Funatsu H - Journal of medical case reports (2009). Not Altered. CC.
Neoplasms of the orbit include: abnormal growth and proliferation of the surrounding tissues of the eye. Neoplasms or tumors of the orbit can either be benign or malignant. Neoplasms of the orbit include the following:
- Capillary hemangioma
- Encapsulated cavernous hemangioma
- Lymphangioma