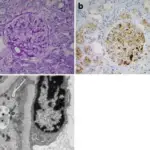
A: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis with glomerular capillary wall collapse, balloon adhesion, and fibrous small new moon body form. Surrounding the open capillary lumen, the mesangial area has no obvious proliferation. (silver staining, 400x). B: Segmental glomerular sclerosis, capillary bundle segmental collapse, balloon adhesion, and cell sex small new moon body form. (PAS staining, 400x). C: HBcAg immunohistochemistry staining: HBcAg along the glomerular capillary wall and mesangial area; stage positive. (400x). D: Immunofluorescence: The glomerulus and mesangial area along the grain; sample fluorescence distribution: LgG-, LgA-, LgM++, C3-, F-, C1q-. HBV reactivation in an occult HBV infection patient treated with prednisone for nephrotic syndrome: case report and literature review: Du W, Zheng Z, Han S, Ma S, Chen S - BMC infectious diseases (2013). Not altered. CC.
Nephrotic syndromes are clinical complexes that includes; massive proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, generalized edema, hyperlipidemia and lipiduria.
Examples of nephrotic syndrome include:
- Dense deposit disease
- Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
- Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
- Membranous nephropathy
- Minimal change disease