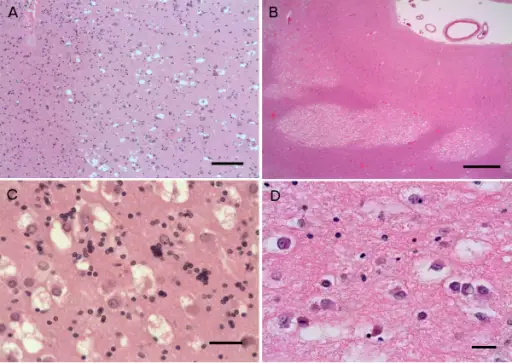
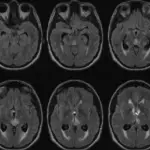
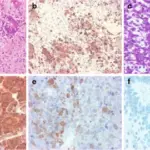
Neuronal tumors are tumors of the central nervous system that contain abnormal neuronal elements.
What is the Pathology of Neuronal Tumor?
Etiology: The causes of neuronal tumors include gene mutations, environmental toxins, and infections.
Pathogenesis: Age is certainly the most common association.
Histology: The histology associated with neuronal tumor shows mitotic figures, clusters of cells embedded in matrix, and increased cellularity.
How does Neuronal Tumor Present?
Patients with Neuronal Tumor are typically males and it is common above 40 years of age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with neuronal tumors include cranial feeling of pressure, headaches, nausea, visual changes, and fatigue.
How is Neuronal Tumor Diagnosed?
Neuronal tumor is diagnosed by by imaging and biopsy.
How is Neuronal Tumor Treated?
Neuronal tumors are treated by surgery with or without chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Neuronal Tumors?
The prognosis of neuronal tumors which are low grade is good. High grade tumors have worse prognosis.