Odontogenic tumors are a group of neoplastic growths that originate from the tissues responsible for tooth formation and the periodontal apparatus of the jaw.
What are Odontomas?
Odontomas are benign tumors linked to tooth development. Specifically, it is a dental hamartoma, meaning that it is composed of normal dental tissue that has grown in an irregular way. It includes both odontogenic hard and soft tissues.
What is the Pathology of Odontomas?
The pathology of odontomas is:
-Etiology: The cause of odontomas is unknown.
-Genes involved:11q13. 3, FGF3, FGF4.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to odontomas is the alteration of differentiated mesenchymal and epithelial odontogenic cells; it has the capacity of forming enamel, dentin, and cement.
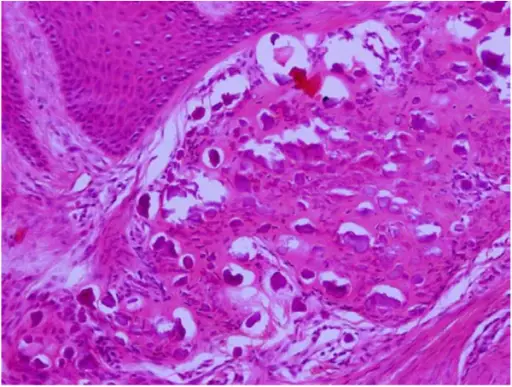
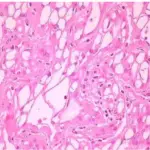
-Histology: The histology associated with odontomas shows scant or occasional ghost cell formation, can cause confusion with COC (CCOT / Gorlin cyst) calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor (CCOT).
How does Odontomas Present?
Patients with odontomas typically affect males and females present in the early range. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with odontomas include asymmetric tooth eruption, malposition, and devitalization.
How are Odontomas Diagnosed?
Odontomas are diagnosed dependent on clinical, radiologic, and pathologic correlation.
How is Odontomas Treated?
Odontomas are treated by excision.
What is the Prognosis of Odontomas?
The prognosis of odontomas is good. Recurrence is uncommon for isolated odontoma.