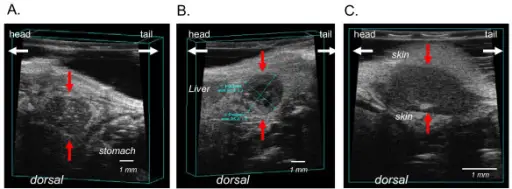
Representative images of pancreatic tumor margins by ultrasound imaging. Difference in echogenity define the tumor from the surrounding tissue. Tumors are hypoechogen (dark-grayish) compared to surrounding tissue. (A) primary orthotopic pancreatic tumor (red arrows). The light coloured specks (hyperechogenic) within the tumor may be microcalcifications or fatty deposits. (B) The cross-sectional area of the primary pancreatic tumor is depicted. The black areas (anechoic) within the tumor are fluid filled cysts correlating to necrotic areas. (C) Peritoneal tumor with surrounding skin.Assessment of anti-inflammatory tumor treatment efficacy by longitudinal monitoring employing sonographic micro morphology in a preclinical mouse model.
Tiwari S, Egberts JH, Korniienko O, Köhler L, Trauzold A, Glüer CC, Kalthoff H - BMC medical imaging (2011). Not Altered. CC.
Pancreatic neoplasms are fluid-filled sacs (cysts) or solid within the pancreas which may benign or malignant.
Examples of pancreatic neoplasms include:
- Acinar cell carcinoma
- Pancreatic carcinoma aka ductal carcinoma of the pancreas
- Pancreatoblastoma
- Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN)
- Cystic neoplasms