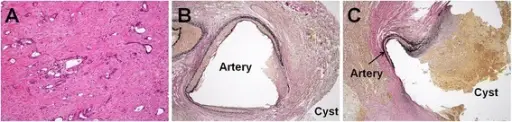
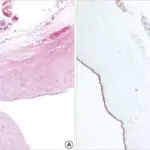
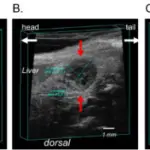
Pancreatic pseudocysts are cysts of the pancreas that are characterized by localized collections of hemorrhagic and necrotic material that lack an epithelial lining.
What is the Pathology of Pancreatic Pseudocysts?
The pathology of pancreatic pseudocysts is: Study of localized fluid collections of hemorrhagic and necrotic material, having a nonepithelialized wall be made up of fibrous and granulation tissue, and generally appears weeks after onset of pancreatitis.
-Etiology: The cause of pancreatic pseudocysts is include acute pancreatitis and pancreatic trauma.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to pancreatic pseudocysts stem from interruptions to the pancreatic duct owing to pancreatitis and eructation of the enzymatic material.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with pancreatic pseudocysts shows varying sizes of 2 to 30 cm diameter sac.
-Histology: The histology associated with pancreatic pseudocysts shows zones of peripancreatic hemorrhagic fat necrosis and fibrous tissue. Pancreatic pseudocysts are characterized by localized collections of hemorrhagic and necrotic material that lack an epithelial lining.
How does Pancreatic Pseudocysts Present?
Patients with pancreatic pseudocysts typically have a male predominance present at an age range of any age group. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with pancreatic pseudocysts include Fever, scleral icterus, pleural effusion a tender abdomen.
How is Pancreatic Pseudocysts Diagnosed?
Pancreatic pseudocysts is diagnosed through laboratory study- amylase and lipase levels elevated. Abdominal ultrasonography, abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan.
How is Pancreatic Pseudocysts Treated?
Pancreatic pseudocysts is treated through medical care-antibiotic therapy, somatostatin analogues, and octreotide. Surgical intervention which may involve catheter drainage, endoscopic drainage may be utilized.
What is the Prognosis of Pancreatic Pseudocysts?
The prognosis of pancreatic pseudocysts is good as most cases resolve without interference.