Pineoblastomas are an aggressive fast-growing, malignant type of cancer, that tend to invade nearby tissue within the brain and spine.
What is the Pathology of Pineoblastomas?
-Etiology: The cause of pineoblastomas is unknown, most occur sporadically, but some have been associated with certain genetic variants.
-Genes involved: Inherited genetic variants in either the RB1 gene or the DICER1 gene.
-Pathogenesis: Pineoblastomas originate from pinealocytes.
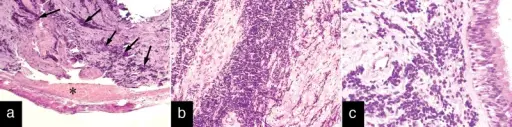
-Histology: The histology associated with pineoblastomas shows sheets of densely packed cells with undifferentiated cells that have minimal cytoplasm and large hyperchromatic nuclei. Necrosis, frequent mitotic figures, and nuclear molding may be present.
How do Pineoblastomas Present?
Patients with pineoblastomas have highest incidence is in childhood, particularly in children less than 2 years old. Because pineoblastomas block CSF flow many symptoms are related to CSF buildup such as headache, nausea, vomiting.
How are Pineoblastomas Diagnosed?
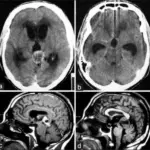
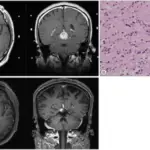
Pineoblastomas is diagnosed thought MRI, CT scanning, CSF puncture and biopsy.
How are Pineoblastomas Treated?
Pineoblastomas first-line therapy is aggressive surgical intervention. Pineoblastomas require postoperative radiotherapy to destroy remaining cancer cells or to slow their growth. Chemotherapy may also be used.
What is the Prognosis of Pineoblastomas?
The prognosis of pineoblastomas is poor, with a 5-year survival of 60%.