Plasma cell neoplasms are diseases in which the body makes too many plasma cells. Plasma cells develop from B lymphocytes (B cells), a type of white blood cell that is made in the bone marrow.
Examples of plasma cell neoplasms and related conditions include:
- Multiple myeloma
- MGUS (monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance)
- Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
- Heavy chain disease
- Primary or immunocyte-associated amyloidosis
- Plasmacytoma
| Plasma cell Neoplasms | Genetics | Key Histologic Findings | Key Clinical Findings |
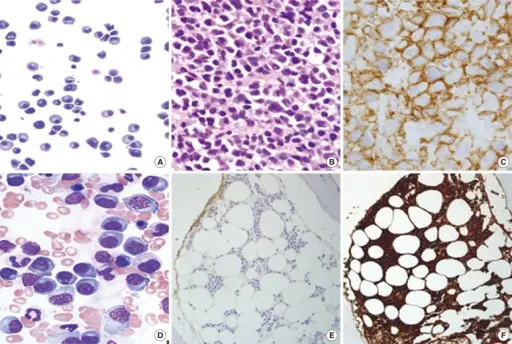
| Multiple myeloma | c-myc gene, N-Ras gene, K-ras gene | Mature myeloma cells usually indistinguishable from normal cells, with a round eccentric cartwheel nucleus without nucleoli, abundant basophilic cytoplasm. Immature myeloma cells have an irregular nucleus with more dispersed chromatin, a higher N/C ratio, and usually prominent nucleoli. | Bone pain, pathologic fractures, spinal cord compression, weakness, malaise, anemia, bleeding, hypercalcemia, kidney failure, and neuropathies. |
| MGUS | DCC gene | Bone marrow <10% plasma cells | Bone pain, fatigue or weakness, unintentional weight loss, fever or night sweats, peripheral neuropathy, enhanced bone loss and fractures. |
| Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia | MYD88 gene | Bone marrow containing variable numbers of pleomorphic lymphoid cells. Dutcher bodies may be seen as intracytoplasmic inclusions positive for periodic acid Schiff. Mast cell hyperplasia is common and may stimulate tumor cell proliferation and monoclonal IgM secretion. | Insidious weakness and mucous membrane bleeding. Some patients have infections, dyspnea, and congestive heart failure. Physical examination may detect pallor, purpura, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly (20%) and engorged retinal veins. |
| Heavy chain disease | Heavy chain gene | Proliferation of B cells and extensive lymphoplasmacytic or plasmacytic infiltrate. | Fever, mild anemia, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), recurrent upper respiratory tract infection, lymphadenopathy, enlarged liver and spleen. |
| Primary or immunocyte-associated amyloidosis | CCND1 (cyclin D1) gene | Amyloid deposition in tissues and organs affected. | Changes in skin color, severe fatigue, feeling of fullness, anemia, joint pain, shortness of breath, tingling and numbness in hands and feet, severe weakness, sudden weight loss. |
| Plasmacytoma | CCND1 gene | Monoclonal cell infiltrates in one or more lytic bone lesions or extramedullary tissue. | Pain in the affected bone, back pain and other consequences of the bone lesion. |