Platelet dysfunctions are a group of bleeding disorders in which the platelets do not function appropriately, leading to bleeding.
What is the Pathology of Platelet Dysfunctions?
The pathology of platelet dysfunctions is:
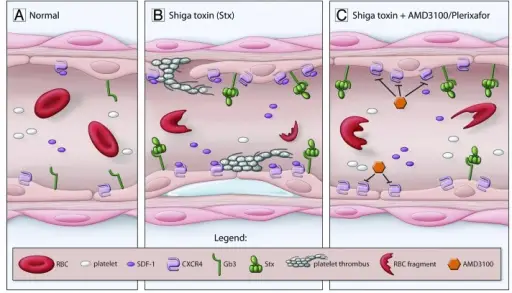
-Etiology: The cause of platelet dysfunctions is a problem in the platelets themselves or to an external factor that alters the function of normal platelets.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to platelet dysfunctions depends on the underlying issue which may include defects to the platelets, defects to platelet receptors, or medication related alterations of platelet activity.
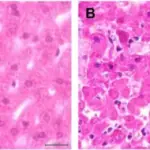
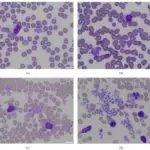
-Morphology: The morphology associated with platelet dysfunctions depends on the underlying cause which may show giant platelets, structural anomalies of platelets, megakaryocyte abnormalities, or alterations of the granules within platelets.
How do Platelet Dysfunctions Present?
Patients with platelet dysfunctions typically are either males or females present in the age range of 6-80 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with platelet dysfunctions typically include increased bruising, nosebleeds, gum bleeding, and prolonged bleeding times.
How are Platelet Dysfunctions Diagnosed?
Platelet dysfunctions are diagnosed using special tests that include:
- Bleeding time
- Platelet function assay
- Platelet aggregation testing
- Platelet electron microscopy
- Genetic testing
How are Platelet Dysfunctions Treated?
Platelet dysfunctions are treated based on the underlying cause.
What is the Prognosis of Platelet Dysfunctions?
The prognosis of platelet dysfunctions is good if properly managed.