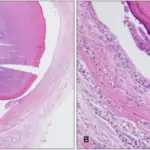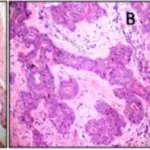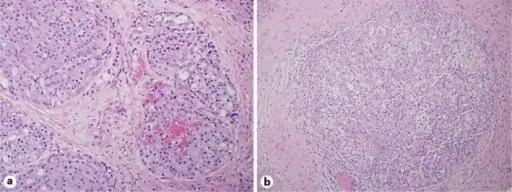
Salivary Gland Neoplasms. a Intermediate-power examination of the recurrent salivary gland tumor in the left neck (H&E. ×100). The tumor cells are relatively monotonous, show round to oval nuclei, and basophilic granular cytoplasm, characteristic of well-differentiated AcCC. b Intermediate-power examination of the metastatic salivary gland tumor in the head of the pancreas (H&E. ×100). Similar to the primary salivary gland tumor, the tumor cells are relatively monotonous and exhibit basophilic granular cytoplasm that is characteristic of well-differentiated AcCC.Acinic cell carcinoma of the salivary gland with metastatic spread to the pancreas.
Geiger JL, García JJ, Price KA - Case reports in oncology (2014). Not Altered. CC.
Salivary neoplasms are among the most cytomorphologically diverse human neoplasms. Among salivary gland neoplasms 80 % arise in the parotid glands, 10 – 15 % arise in the submandibular glands, and the remainder arise in the sublingual and minor salivary glands.
Salivary gland neoplasms can be benign or malignant.
Examples of Benign salivary gland neoplasms include:
- Basal cell adenoma
- Canalicular adenoma
- Ductal papillomas
- Pleomorphic adenoma
- Oncocytoma
- Warthin tumor