Serous cystic neoplasms are benign cystic tumors having glycogen-rich, low-cuboidal cells surrounding trivial cysts comprising a clear, thin, straw-colored fluid, accounting for about 25% of pancreas cystic neoplasms.
What is the Pathology of Serous Cystic Neoplasms?
The pathology of serous cystic neoplasms is:
-Etiology: The cause of serous cystic neoplasms is not well understood.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to serous cystic neoplasms is not well understood.
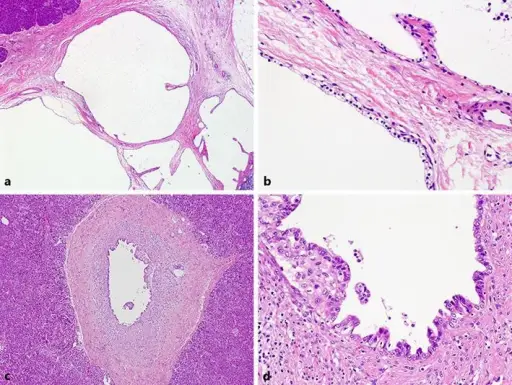
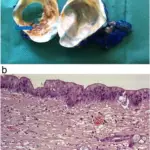
-Morphology: The morphology associated with serous cystic neoplasms shows masses of varying sizes up to 20 cm, containing serous fluid.
-Histology: The histology associated with serous cystic neoplasms shows it is lined with flattened or cuboidal epithelium, dense fibronodular scar composed of acellular hyalinized tissue, and tiny cysts of cuboidal epithelial cells.
How does Serous Cystic Neoplasms Present?
Patients with serous cystic neoplasms typically common in females than males, present at an age range of 7th decade. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with serous cystic neoplasms include nonspecific abdominal pain, abdominal masses.
How is Serous cystic neoplasms Diagnosed?
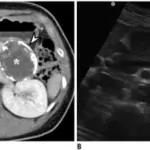
Serous cystic neoplasms are diagnosed through clinical presentation and radiological studies- CT scan, and MRI.
How is Serous Cystic Neoplasms Treated?
Serous cystic neoplasms is treated through surgical resection.
What is the Prognosis of Serous Cystic Neoplasms?
The prognosis of serous cystic neoplasms is fair.