Sertoli cell tumors are rare tumor derivatives of Sertoli cells, situated in seminiferous tubules, that support spermatogenesis.
What is the Pathology of Sertoli Cell Tumors?
The pathology of Sertoli cell tumors is:
-Etiology: The cause of Sertoli cell tumors is unknown
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Sertoli cell tumors unknown
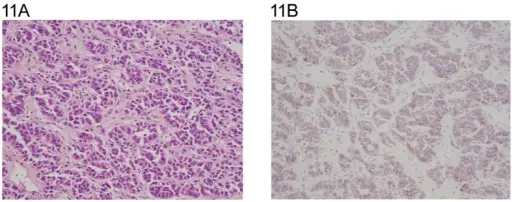
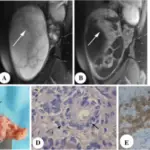
-Morphology: The morphology associated with Sertoli cell tumors shows firm, small nodules with a standardized gray-white to the yellow cut surface.
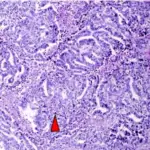
-Histology: The histology associated with Sertoli cell tumors shows lesion cells are arranged in typical trabeculae with an inclination to form cordlike structures like undeveloped seminiferous tubules.
How does Sertoli Cell Tumors Present?
Patients with Sertoli cell tumors are typically males that present within an age range of 16 to 45 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Sertoli cell tumors include testicular mass, impotence, and gynecomastia.
How is Sertoli Cell Tumors Diagnosed?
Sertoli cell tumors is diagnosed by laboratory testing and biopsy.
How is Sertoli Cell Tumors Treated?
Sertoli cell tumors is treated, through medical care, chemotherapy, and surgical resection.
What is the Prognosis of Sertoli Cell Tumors?
The prognosis of Sertoli cell tumors is good when diagnosed and treated while still benign.