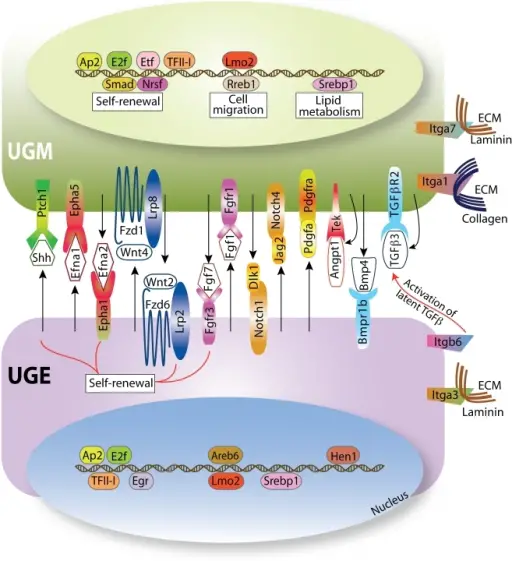
Signal Transduction Pathways. The signal transduction pathways expressed in the prostate stem cell niche.Ligand-receptor interactions and transcription factors that are differentially expressed between the UGE and the UGM are depicted. These are the main mediators of the cellular cross-talk between these two compartments in the prostate stem cell niche. These mediators include members of the Shh, Wnt/β-catenin, Notch, FGF and TGF-β signaling pathways that are important regulators of stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Transcriptional regulators whose binding motifs are enriched in the differentially expressed genes are depicted in the nucleus. Activation of these transcription factors promotes expression of genes that are involved in self-renewal, lipid metabolism and cell migration. Many of these factors are implicated in the progression of prostate tumors as their expression is increased (e.g., Wnt/β-catenin genes) or decreased (e.g., Notch genes). Molecular signatures of the primitive prostate stem cell niche reveal novel mesenchymal-epithelial signaling pathways. Blum R, Gupta R, Burger PE, Ontiveros CS, Salm SN, Xiong X, Kamb A, Wesche H, Marshall L, Cutler G, Wang X, Zavadil J, Moscatelli D, Wilson EL - PloS one (2010). Not Altered. CC.
Signal transduction pathways are pathways by which a cell responds to substances outside the cell through signalling molecules found on the surface of and inside the cell.
Examples of signal transduction pathways include:
- Kinase activity in signal transduction pathways involve controlling cell growth and proliferation to the initiation and regulation of immunological responses
- Tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell
- G-protein coupled receptors act like an inbox for messages in the form of light energy, peptides, lipids, sugars, and proteins
- Nuclear receptors are a family of ligand-regulated transcription factors that are activated by steroid hormones, such as estrogen
- Wnt protein ligands are secreted glycoproteins that are cysteine-rich and highly hydrophobic which bind to N-terminal extra-cellular cysteine-rich domain
- Notch family receptors are cell-surface receptors that transduce short-range signals by interacting with transmembrane ligands