Stem cell transplant also called one marrow transplant, is the procedure involving the replacement of damaged stem cells in the patient with healthy stem cells. The new stem cells can be taken from the patient’s own healthy stem cells or from a healthy donor. The use of hematopoietic stem cells is very common in which stem cells are introduced into the bloodstream of the patient after conditioning the patient. A potential risk of hematopoietic stem cells is graft versus host disease.
What are Stem Cell Transplants?
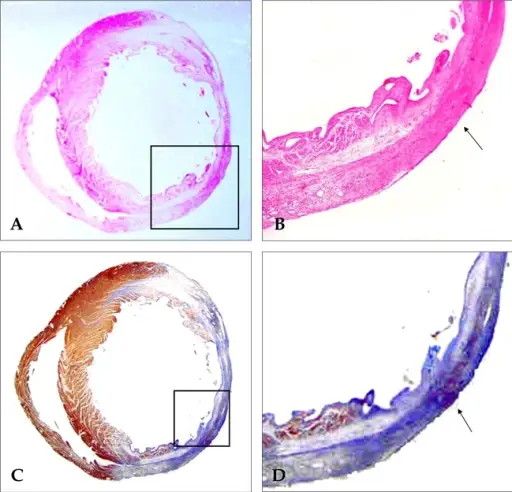
Stem Cell Transplant. Microscopic appearance of a cryo-infarct in a stem cell transplanted rat heart (Fig. 4). (A) H & E staining revealed cells in the mononuclear stem cell implant site. (B) Magnified view of the box in A. The stem cell transplant site had a higher density of cells (arrow). (C) With Masson Trichrome staining, a huge amount of fibrosis was observed from 1 to 6 o'clock along the left ventricle after the cryo-infarction (blue color). The stem cell transplant site had a brown color (box). (D) Magnified view of the box in C. The stem cell transplant site had less fibrosis (brown color, arrow). Not Altered. CC.
Bone marrow mononuclear stem cells transplanted in rat infarct myocardium improved the electrical conduction without evidence of proarrhythmic effects.
Joung B, Kim IK, Lee MH, Yoo KJ, Kim SS