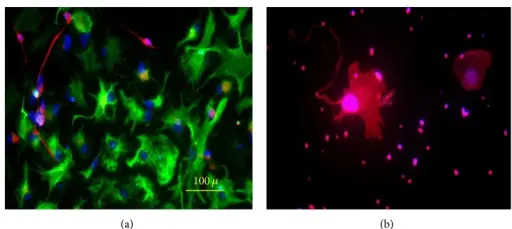
(a) Neurons and astrocytes differentiated from breast milk stem cells-derived neural stem cell stained with anti-β-tubulin-Alexa Flour 568 (red) and anti-GFAP-Alexa Flour 488 (green); (b) oligodendrocyte differentiated from breast milk stem cell-derived neural stem cell stained with anti-O4-Alexa Flour 568. Differentiation of human breast-milk stem cells to neural stem cells and neurons. Hosseini SM, Talaei-Khozani T, Sani M, Owrangi B - Neurology research international (2014). Not altered. CC.
Stem cells are basic cells that can become almost any type of cell in the body under specific conditions.
Embryonic stem cells are derived from the undifferentiated inner mass cells of a human embryo they are pluripotent, meaning they are able to grow.
Tissue stem cells are undifferentiated cell, capable of proliferation, self-renewal, production of a large number of differentiated functional progeny, regenerating tissue after injury.