Struma ovarii teratomas are specialized or monodermal teratoma predominantly composed of mature thyroid tissue.
What is the Pathology of Struma Ovarii Teratomas?
The pathology of struma ovarii teratomas is:
-Etiology: The cause of struma ovarii teratomas is unknown.
-Genes involved: BRAF gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to struma ovarii teratomas is unknown.
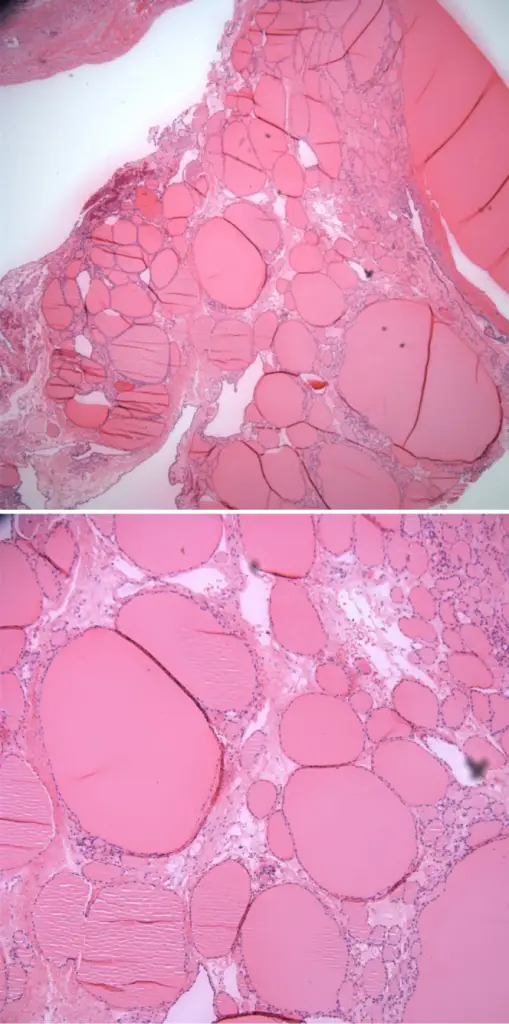
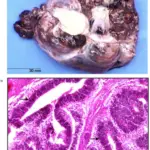
-Morphology: The morphology associated with struma ovarii teratomas shows peritoneal or pleural effusion mass.
-Histology: The histology associated with struma ovarii teratomas shows thyroid microfollicles with a single cell lining, overlapping nuclei, rare mitotic figures.
How does Struma Ovarii Teratomas Present?
Patients with struma ovarii teratomas typically females between 40-60 years age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with struma ovarii teratomas include: pain and/or a pelvic mass and less frequently with ascites, hyperthyroidism, absence of thyroid gland enlargement, an elevated thyroglobulin level.
How is Struma Ovarii Teratomas Diagnosed?
Struma ovarii teratomas is diagnosed by: thyroid function tests, ultrasound, CT scan.
How is Struma Ovarii Teratomas Treated?
Struma ovarii teratomas is treated by: surgery, laparoscopy, hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy in post menopausal women.
What is the Prognosis of Struma Ovarii Teratomas?
The prognosis of struma ovarii teratomas is excellent. The prognosis of malignant type disease is not well-characterized, given the rarity of this disease.