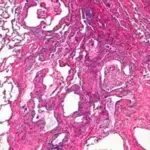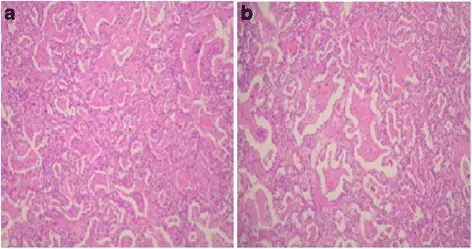
Panels a and b are different plates from the lung biopsy showing pulmonary alveolar proteinosis pattern characterized by type II pneumocytes hyperplasia, interstitial widening, and fine granular proteinosis material admixed with foamy macrophages. Fatal respiratory disease due to a homozygous intronic ABCA3 mutation: a case report. Journal of Medical Case Reports. Not Altered. CC.
Surfactant dysfunction disorders that cause restrictive lung diseases are a group of conditions that result from anomalies in the surfactant function or composition.
Examples of surfactant dysfunction disorders that cause restrictive lung diseases are:
Disorders due to mutations in genes involved in surfactant secretion or trafficking.