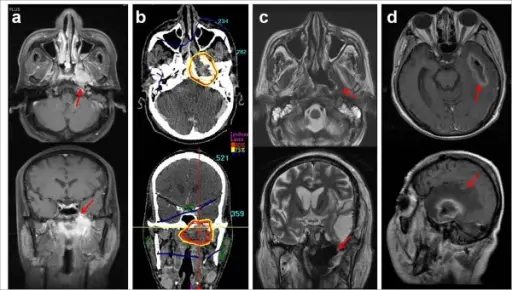
Left nasopharyngeal wall soft tissue necrosis and temporal lobe necrosis after SBRT. This patient was a 48-year-old male with type I NPC (T4N2M0) (a). He was treated with cisplatin-based concurrent chemoradiation via EBRT up to 70.2 Gy followed by SBRT at 21 Gy in 3 fractions due to persistent disease in the left skull base (b). Although he achieved CR and no loco-regional or distant metastasis occurred, left nasopharyngeal wall soft tissue necrosis (c) and temporal lobe necrosis (d) developed 4.4 and 7.2 months after SBRT, respectively. Long-term outcome and toxicity of hypofractionated stereotactic body radiotherapy as a boost treatment for head and neck cancer: the importance of boost volume assessment: Lee DS, Kim YS, Cheon JS, Song JH, Son SH, Jang JS, Kang YN, Kang JH, Jung SL, Yoo IeR, Jang HS - Radiation oncology (London, England) (2012). Not altered. CC.
Caseous necrosis.
Coagulative necrosis.
Fat necrosis.
Gangrenous necrosis.
Liquefactive necrosis.
