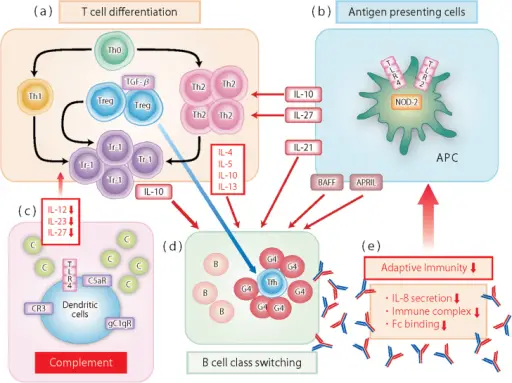
Cross-talk between innate and acquired immunity in IgG4-RD. (a) T-cell differentiation (acquired immunity). Naive helper T cells (Th0) can become either Th1 or Th2 under the instructive influence of IL-12 or IL-4, respectively. Th2 cells produce IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13, which are potent activators of B-cell IgE production and eosinophil recruitment. In addition, TGF-β induces Foxp3 and generates Treg cells. Whereas, Tr1 cells, an important source of IL-10, are converted from Th1, Th2 and Treg cells by IL-27. (b) Antigen-presenting cells (innate immunity). TLR4 recognizes LPS, which is unique to Gram-negative bacteria, whereas TLR2 is activated by lipoteichoic acid (LTA) or bacterial lipoproteins. Ligation of TLR2 by pathogenic micro-organisms such as fungi and mycobacteria induces a Th2 anti-inflammatory bias, either through release of IL-10 or through inhibition of IFN-γ signaling. IL-27 is produced primarily by antigen-presenting cells after stimulation by microbial products or inflammatory mediators and converts activated inflammatory CD4+ T cells into IL-10-producing Tr1 cells. The activation of TLRs or NLRs (NOD-2) in APCs produces BAFF and APRIL, leading to IgG4 production. (c) Cross-talk between the complement system and TLRs (innate immunity). C3 activation generates effector molecules such as C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins, which activate specific G-protein-coupled receptors, CR3 and C5aR, respectively. Activation of C5aR in macrophages and dendritic cells inhibits TLR-4-induced production of IL-12, IL-23 and IL-27 proteins from these cells. This decreased cytokine response translates into a decreased Th1 response as an important mechanism for a shift of Th1 to Th2 polarization in response to innate and adaptive immune network activation. (d) B-cell immunoglobulin class switching to IgG4 (acquired immunity). Most antigens initiate class switching and SHM in the GC of lymphoid follicles through cognate interaction between B cells and Tfh cells that express CD40 ligand (CD40L). Tfh cells provide crucial signals to GC B cells undergoing SHM and selection that results in affinity maturation. BAFF and APRIL, in concert with IL-21, enhance IgG4 production via promoting the expansion of IgG4-committed B cells. The survival of B cells committed to IgG4 production is enhanced in the presence of IL-21. (e) Impairment of adaptive immunity (innate immunity). IgG4 antibodies can exchange Fab arms by swapping a heavy chain and attached light chain and form bispecific antibodies. The interactions of IgG4 with the Fcγ receptor and C1q are weaker than those of other IgG subclasses, resulting in blocking Fc-mediated effector functions of IgG1, inhibiting the formation of large immune complexes and decreasing IL-8 excretion from neutrophils. These properties of the IgG4 mediate impaired adaptive immunity. IgG4-related disease and its pathogenesis-cross-talk between innate and acquired immunity. Umehara H, Nakajima A, Nakamura T, Kawanami T, Tanaka M, Dong L, Kawano M - International immunology (2014). Not Altered. CC.
Reactions of innate immunity are inflammation, antiviral defines, signal generation.
Inflammation is a process by which your body’s white blood cells and the things they make protect you from infection from outside invaders, such as bacteria and viruses.
Antiviral defines: Protein synthesized or activated in the cell in response to viral infection, or protein with specific antiviral activity within the cell.
Signal generation is done by molecules released by stressed cells undergoing necrosis that act as endogenous danger signals to promote and exacerbate the immune and inflammatory response.