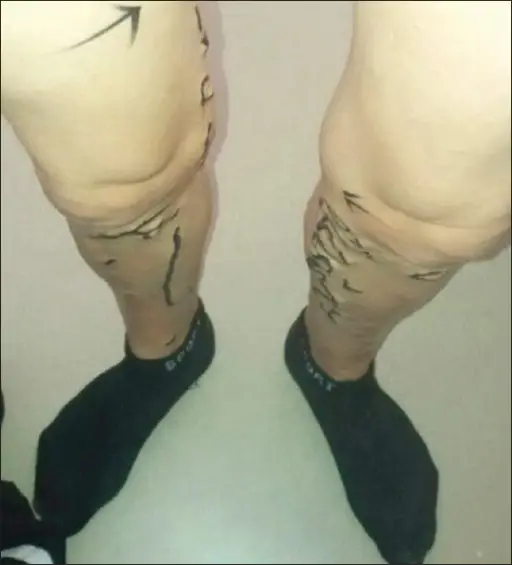
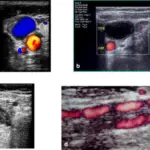
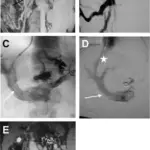
Varicose veins are tortuous and permanently dilated superficial veins of the lower extremities.
What is the Pathology of Varicose Veins?
The pathology of varicose veins is:
-Etiology: The cause of varicose veins is familial factors, venous hypertension, hormonal effects on smooth muscle, obesity, chronic constipation.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to varicose veins are as a result of familial tendency toward premature varicosities, increased venous pressures leading to venous stasis, and pedal edema.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with varicose veins shows dilated, tortuous,
elongated and nodular of the affected vein.
-Histology: The histology associated with varicose veins shows inconstant fibromuscular thickening of the vein wall.
How does Varicose Veins Present?
Patients with varicose veins are typically older females. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with varicose veins include thrombosis, congestion, pain, ulcerations, ill healing lesions and edema in the extremity.
How is Varicose Veins Diagnosed?
Varicose veins is diagnosed through medical therapy and surgical- stab phlebectomy, excision of small saphenous vein, and endovenous laser treatment.
How is Varicose Veins Treated?
Varicose veins is treated through physical exam and duplex ultrasonography.
What is the Prognosis of Varicose Veins?
The prognosis of varicose veins is good proper treatment arrests the progression of the condition.