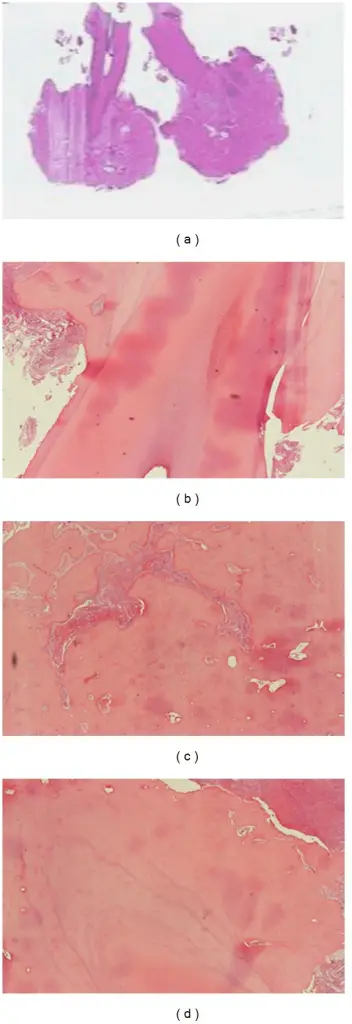
Cementoblastoma is a relatively rare benign neoplasm of the cementum of the teeth. It is derived from ectomesenchyme of odontogenic origin.
What is the Pathology of Cementoblastoma?
The pathology of cementoblastoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of cementoblastoma is unknown and is linked with many sources, including trauma, nutritional deficiency, metabolic disturbances, and constitutional factors.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to cementoblastoma develop as cells that generate cementum, or cementoblasts uncontrollably proliferate at the apex of a tooth root. Cementoblasts that form the cementum typically cease activity and become cementocytes.
-Histology: The histology associated with cementoblastoma shows large cementicles (globules) fused to form a mass within the proliferative fibrovascular stroma.
How does Cementoblastoma Present?
Patients with Cementoblastoma typically affect males and females present in the age range of 20-30 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with cementoblastoma include dull pain and dentin hypersensitivity can occur as growth increases. Visibility of the cementoblastoma may increase with growth and cause distortion/swelling to the face and surrounding areas along with tooth displacement.
How is Cementoblastoma Diagnosed?
Cementoblastoma is diagnosed using a radiograph in which it shows dense homogenous mass continuous with tooth root.
How is Cementoblastoma Treated?
Cementoblastoma is treated by surgically removing the mass and possibly a portion of the affected area and/or teeth.
What is the Prognosis of Cementoblastoma?
The prognosis of cementoblastoma is good.