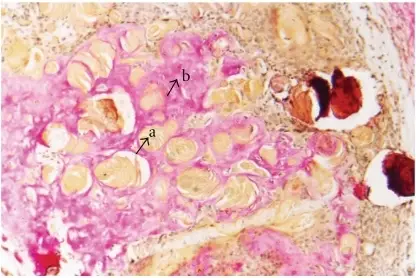
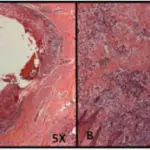
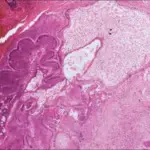
Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor is a locally invasive neoplasm that is characterized by ameloblastoma-like epithelial islands, ghost cells, and dentoid.
What is the Pathology of Dentinogenic Ghost Cell Tumor?
The pathology of dentinogenic ghost cell tumor is:
-Etiology: The cause of dentinogenic ghost cell tumor is unknown.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to dentinogenic ghost cell tumor is the signaling pathway that has a role in the development similar to calcifying odontogenic cyst since beta-catenin gene mutations and beta-catenin overexpression is also identified in DGCT.
-Histology: The histology associated with dentinogenic ghost cell tumor shows solid mass consisting of sheets of anastomosing cords and strands of the odontogenic epithelium; microcystic development is possible.
How does Dentinogenic Ghost Cell Tumors Present?
Patients with dentinogenic ghost cell tumors typically affect males and females present in the age range of 11-79 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with dentinogenic ghost cell tumors include they are asymptomatic.
How are Dentinogenic Ghost Cell Tumors Diagnosed?
Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor is diagnosed by radiologic and histopathologic correlation
How are Dentinogenic Ghost Cell Tumors Treated?
Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor is treated simple enucleation, curettage
What is the Prognosis of Dentinogenic Ghost Cell Tumors?
The prognosis of dentinogenic ghost cell tumors is poor.