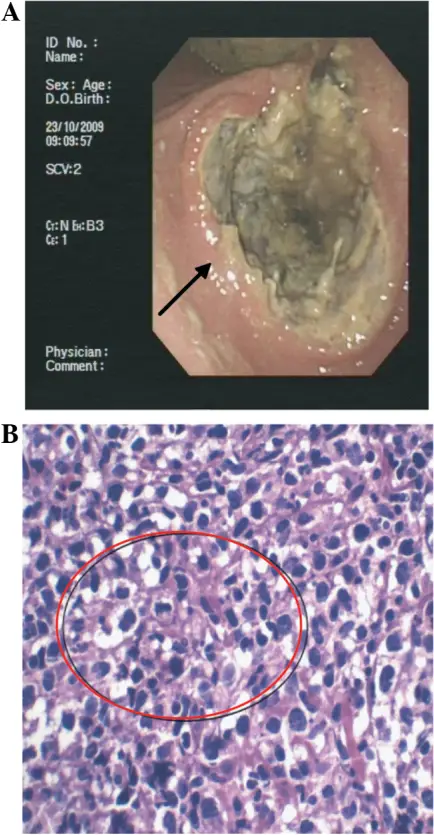
Gastric lymphoma is a general term for a type of cancer that originates within the stomach. Approximately 90 percent of patients of primary gastric lymphoma are either mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue MALT gastric lymphoma or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma DLBCL of the stomach.
What is the Pathology of Gastric Lymphoma?
The pathology of gastric lymphoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of gastric lymphoma is unknown. However, a strong association between infection with Helicobacter pylori H. pylori and the development of MALT gastric lymphoma has been established.
-Genes involved: CDH1.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to gastric lymphoma are: Pathogenesis is often related to Helicobacter pylori infection. When these cells are continuously stimulated by H pylori, they can give rise to lymphomas. In addition to B cells, T cells and macrophages play an important role in MALT lymphomagenesis.
-Histology: The histology associated with gastric lymphoma shows lymphoepithelial lesions formed by the invasion of individual crypts by aggregates.
How does Gastric Lymphoma Present?
Patients with gastric lymphoma typically in males present at age range of 60-65 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with gastric lymphoma include unintended weight loss, fatigue, low levels of circulating red blood cells anemia, abdominal and/or back pain, loss of appetite anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and/or constipation. In some cases, it may be possible to feel a mass in the abdomen.
How is Gastric Lymphoma Diagnosed?
Gastric lymphoma is diagnosed by biopsy at the time of endoscopy, blood tests, bone marrow aspirates, and specialized imaging tests.
How is Gastric Lymphoma Treated?
Gastric lymphoma is treated by antibiotic therapy, surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. These treatments may be used alone or in varied combinations.
What is the Prognosis of Gastric Lymphoma?
The prognosis of gastric lymphoma is good. Low-grade gastric lymphomas involving the mucosa and submucosal layers carry a favorable prognosis with up to 90% survival at 10 years.