A gastrinoma is a type of tumor that leads to increased production of gastric acid secretion located at the head of the pancreas.
What is the Pathology of Gastrinoma?
The pathology of gastrinoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of gastrinoma is excess gastrin secretions.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: Excess gastrin secretion.
-Morphology: None.
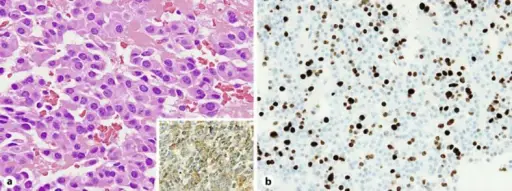
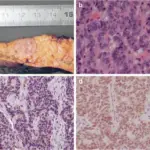
-Histology: The histology associated with gastrinoma shows bland and rare cases of anaplasia, well-differentiated lesional cells.
How does Gastrinoma Present?
Patients with gastinoma typically more in males present at an age range of 30-50 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings of gastrinoma include abdominal pain, diarrhea, steatorrhea, weight loss, gastroesophageal reflux.
How is Gastrinoma Diagnosed?
Gastrinoma is diagnosed by secretin stimulation test, basal acid output >10mEq/h, fasting hypergastrinemia, fasting serum gastrin levels, somatostatin receptor scintigraphy, CT scan and MRI.
How is Gatrinoma Treated?
Gastrinoma is treated by symptom management. Chemotherapy, surgical care, and frequent long-term monitoring may be required.
What is the Prognosis of Gastrinoma?
The prognosis of gastrinoma is fair, with a survival rate of 5-years being 20-30%.