A glandular odontogenic cyst is a rare and uncommon jaw bone cyst of odontogenic origin. It is a cyst having an unpredictable, potentially aggressive behavior, and has the propensity to grow in large size with a relatively high recurrence rate.
What is the Pathology of Glandular Odontogenic Cyst?
The pathology of glandular odontogenic cyst is:
-Etiology: The cause of glandular odontogenic cyst is origin is rested of the dental lamina
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to glandular odontogenic cyst cellular mutation, cyst maturation at glandular, BCL-2 protein.
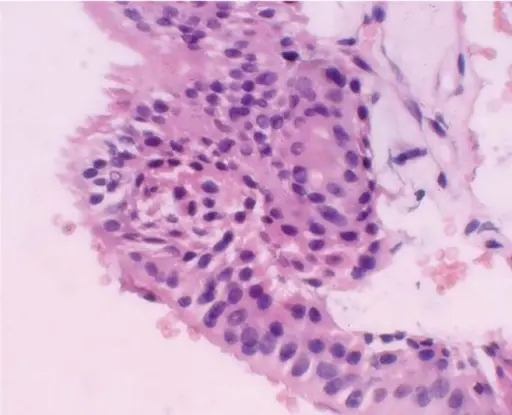
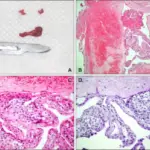
-Histology: The histology associated with glandular odontogenic cyst shows nonkeratinized or slightly basaloid epithelial cyst lining which may exhibit a number of microscopic parameters.
How does the Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Present?
Patients with Glandular Odontogenic cysts typically affect males and females present in the age range of 40-60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Glandular Odontogenic cyst include Jaw expansion, swelling, impairment to the tooth, root, and cortical plate.
How is Glandular Odontogenic cyst Diagnosed?
Glandular Odontogenic cyst is diagnosed by biopsy, CT scans, and panoramic x-rays.
How is Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Treated?
Glandular Odontogenic cyst is treated by enucleation, curettage, marginal or partial resection, marsupialization
What is the Prognosis of Glandular Odontogenic cyst?
The prognosis of glandular odontogenic cyst is poor.