Glomus tumor is also known as glomangioma, a painful benign growth originating from specialized smooth muscle cells of glomus bodies, arteriovenous structures tangled in thermoregulation.
What is the Pathology of Glomus Tumor?
The pathology of glomus tumor is:
-Etiology: The cause of glomus tumor is glomus cells proliferation.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to glomus tumor not well known as event of glomus cell propagation is unknown.
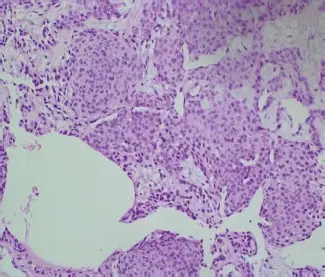
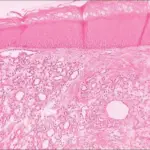
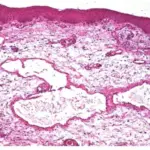
-Morphology: The morphology associated with glomus tumor shows solitary well-circumscribed nodules lesion.
-Histology: The histology associated with glomus tumor shows unvaryingly round, trivial, glomus cells having pale eosinophilic cytoplasm.
How does Glomus Tumor Present?
Patients with glomus tumor typically have no sex predilection and present at age range of 20 to 40 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with glomus tumor include trivial, blue/red papules or nodules at the distal extremities.
How is Glomus Tumor Diagnosed?
Glomus tumor is diagnosed through clinical presentation and histologic findings.
How is Glomus Tumor Treated?
Glomus tumor is treated through surgical excision.
What is the Prognosis of Glomus Tumor?
The prognosis of glomus tumor is good with proper management surgical excision.