Glucagonoma is a disease of the pancreas that leads to increased production of the glucagon hormone in the blood.
What is the Pathology of Glucagonoma?
The pathology of glucagonoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of glucagonoma is unclear but can be due to familial inheritance.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to glucagonoma is uncertain.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with glucagonoma shows a single solid mass with well-marked boundaries.
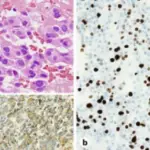
-Histology: The histology associated with glucagonoma shows tumor cells organized in nests and strands.
How does Glucagonoma Present?
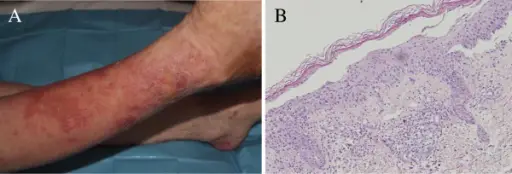
Patients with glucagonoma, are typically males and females, at an age range of 20-84 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with glucagonoma include diarrhea but can be asymptomatic during the early stages, weight loss, stomatitis. Glucagonoma is associated with a characteristic rash called necrolytic migratory erythema.
How is Glucagonoma Diagnosed?
Glucagonoma is diagnosed by radioimmunoassay, fasting blood sugar and glucose tolerance test, complete blood count, angiography, and CT scan.
How is Glucagonoma Treated?
Glucagonoma is treated according to the stage of the disease, debulking, surgical resection, long-acting octreotide, and embolization.
What is the Prognosis of Glucagonoma?
The prognosis of glucagonoma is poor if metastasis has occurred.