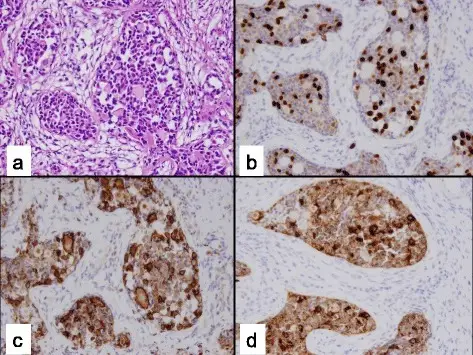
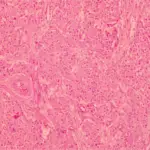
Gonadoblastoma is a rare ovarian lesion that consists of germ cells that resemble those of dysgerminoma and gonadal stroma cells and are benign but sometimes may become malignant.
What is the Pathology of Gonadoblastoma?
The pathology of gonadoblastoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of gonadoblastoma is abnormal chromosomal karyotype, gonadal dysgenesis
-Genes involved: 46,XY; 45,X/46,XY; or 45,XO karyotypes
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to gonadoblastoma are: Gonadal differentiation starts after 5 weeks of gestation and depends on sex chromosome of fetus, errors in this complex multistep process of sexual differentiation may cause dysgenetic gonads.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with gonadoblastoma shows bilateral, tumors usually small and may be microscopic
-Histology: The histology associated with gonadoblastoma shows Nests of dysgerminoma-like germ cells, Hyalinization and calcification
How does Gonadoblastoma Present?
Patients with gonadoblastoma typically in females at age younger than 30 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with gonadoblastoma include: distension of abdomen, excessive hair growth over the body and hoarseness of voice, hirsutism, intraabdominal mass, abnormal menstruation.
How is Gonadoblastoma Diagnosed?
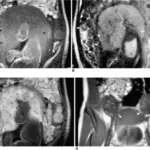
Gonadoblastoma is diagnosed by: ultrasound, CT scan, blood tests for tumor markers, beta hCG and testosterone levels, laparotomy, bilateral oophorectomy and hysterectomy
How is Gonadoblastoma Treated?
Gonadoblastoma is treated by: local excision, adjuvant chemotherapy
What is the Prognosis of Gonadoblastoma?
The prognosis of gonadoblastoma is excellent if no malignancy. Successful pregnancy has been achieved in patients with gonadal dysgenesis following stimulation of uterine growth with cyclical hormone replacement.