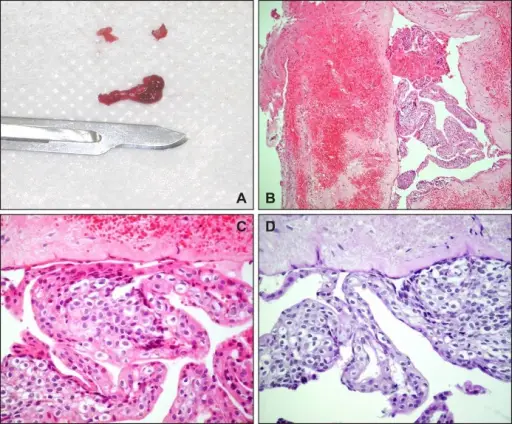
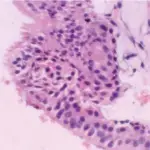
A lateral periodontal cyst is a non-keratinized and non-inflammatory developmental cyst located adjacent or lateral to the root of a vital tooth
What is the Pathology of Lateral Periodontal Cyst?
-Etiology: The cause of lateral periodontal cyst is from epithelial rests in the periodontal ligament
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to lateral periodontal cyst remains controversial, with extensive debate in the literature over the different hypotheses.
-Histology: The histology associated with lateral periodontal cyst shows cystic lumens with thick linings.
How does a Lateral Periodontal Cyst Present?
Patients with Lateral Periodontal cysts typically affect males and females present in the age range of 50-70 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with lateral periodontal cyst include a small, soft-tissue swelling found just below or within the interdental papilla. However, as it is usually asymptomatic in nature, LPCs are usually detected through radiography.
How is Lateral Periodontal Cyst Diagnosed?
Lateral Periodontal cyst is diagnosed in routine radiography.
How is the Lateral Periodontal Cyst Treated?
Lateral Periodontal cyst is treated by enucleation, curettage, or excision with preservation of adjacent teeth is adequate for conventional LPC
What is the Prognosis of Lateral Periodontal cyst?
The prognosis of lateral periodontal cyst is good with rare recurrence.